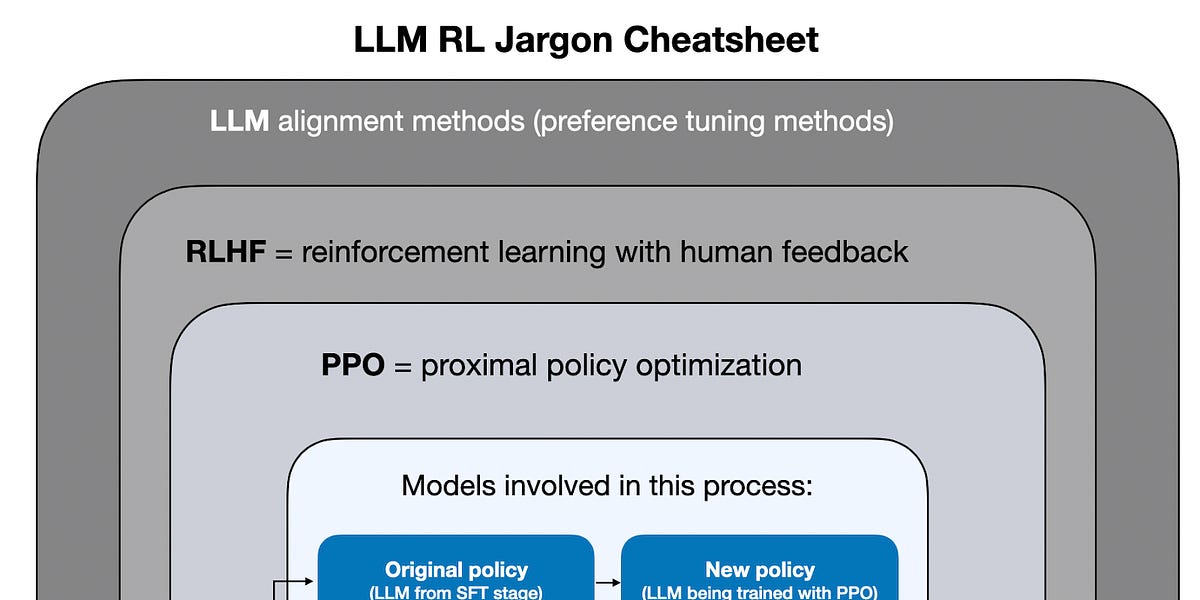
Headquartered in Boston, enterprise AI company DataRobot recently unveiled its enterprise AI suite to simplify the creation and deployment of AI applications. The AI suite helps develop and deliver generative AI applications and agents.
A few weeks prior to the launch, AIM got in touch with CEO Debanjan Saha, who discussed the company’s strategy of addressing three critical gaps hindering widespread AI adoption in enterprises: the value gap, the confidence gap, and the expertise gap.
Addressing the Value Gap
Saha emphasised the need for AI investments to deliver tangible business value. “People are building data centres. At various conferences, you will hear that people are building gigawatts of capacity,” Saha noted.
However, he stressed that these investments must translate into solving real business problems beyond creating simple chatbots.
To bridge this gap, DataRobot is focusing on helping customers identify and implement AI use cases that drive significant business impact.
“Often, in order to take an AI use case to production, from ideation to final stage, there are 19 different teams who have to participate in a collaborative way to make it through that process,” Saha revealed, highlighting the complexity of implementing AI solutions at scale.

Tackling the Confidence Gap
The confidence gap, as described by Saha, stems from various risks associated with AI deployment, including operational, accuracy, reputational, and regulatory risks. Due to these concerns, many organisations are hesitant to move beyond prototypes and demos.
DataRobot has implemented robust governance and monitoring features in its enterprise AI suite to address this gap. For regulated industries such as financial services, the company provides comprehensive AI governance, such as AI observability with real-time intervention and moderation and one-click compliance documentation to empower businesses to deploy AI with confidence.
“Before AI can go into production, it has to go through a set of checks, and a compliance report needs to be produced for both internal auditors and external regulatory bodies,” Saha explained. This approach has made DataRobot particularly attractive to financial institutions, with 60% of the top banks in the United States using the enterprise AI suite.
Closing the Expertise Gap
Having recognised the scarcity of AI talent, especially in enterprises, DataRobot is working to make AI more accessible to a broader range of professionals. The company’s strategy involves both technological solutions and hands-on support.
On the tech front, the enterprise AI suite aims to lower the bar for participation through automation and user-friendly interfaces. Additionally, the company offers executive sessions, ideation workshops, and supervised hackathons.
“We have a team of highly-skilled data scientists who have years of experience working with customers even before generative AI to help solve business use cases with AI,” Saha said. These specialists, known as applied AI experts, work alongside customer teams to upskill and assist them in implementing AI projects.
Bridging Predictive,Generative AI, and Agentic AI
It was in response to these gaps that DataRobot introduced the enterprise AI suite. It includes composable AI applications and agents that can be customised for a wide range of business needs, from predictive data analysis to generative content creation. The suite also features a collaborative AI application library, allowing teams to work together from a central repository, sharing tools, insights, and solutions.
This collaboration is central to the enterprise AI suite, as it encourages cross-functional teams to innovate together and scale AI applications quickly. Developers can easily prototype, test, and refine generative AI applications, benefiting from real-time insights and accelerated deployment.
The enterprise AI suite also streamlines the process of publishing and monitoring applications, ensuring that updates and improvements are implemented without user downtime, and that inputs remain accurate and up to date.
Meanwhile, DataRobot has introduced advanced AI observability features, including “guard models” for generative AI applications. These guards intercept prompts and responses, checking for issues such as data leaks, toxicity, and accuracy.
“We have put together a set of what we call ‘guard models’. So, when you deploy an LLM (foundational or fine-tuned), for example, you can deploy that with a set of guard models around it,” Saha explained. This approach allows for real-time intervention based on predefined rules, enhancing the safety and reliability of AI applications in production environments.
DataRobot AI applications are already delivering value for customers and partners. “DataRobot is enabling teams to deploy AI 83% faster than traditional methods and reduce costs by up to 80%,” said Saha. With over 38,000 customer deployments, global organizations including CVS Health, BMW Group, and the U.S. Army rely on DataRobot for AI that makes sense for their business
In India, DataRobot has already proven success with increased productivity and accelerated value from AI. “DataRobot is an extreme developer productivity multiplier. We helped Razorpay to go from five days to less than four hours to create each model.” noted Saha.

 3 weeks ago
11
3 weeks ago
11